Introduction
Urban planning and development have been transformed by Geographic Information Systems (GIS), which provide strong tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data. As cities around the world continue to grow, GIS technology has become indispensable for city planners, architects, and policymakers. Through its ability to integrate various datasets and create detailed visualizations, GIS allows stakeholders to make informed decisions that promote sustainable, efficient, and equitable urban development. We will explore the role of GIS in modern urban planning and development, highlighting its applications, benefits, and future potential.
Definition
A system known as geographic information is used to analyze, create, preserve, and map different types of data. It also links to the map through the integration of location data with several kinds of descriptive data, including demographic data. Thanks to technology, it is now feasible to analyze, understand, and visualize geographic data in order to find trends, patterns, and appropriate investments. With GIS, users can gain a deeper understanding of spatial context, patterns, and relationships. Recently, the most important function of this technology has been mapping.
Understanding GIS and Its Core Components
GIS is a digital system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. It integrates hardware, software, and data, enabling users to visualize geographic patterns, relationships, and trends in a variety of formats, including maps, 3D models, and interactive dashboards.
GIS Applications in Urban Planning
GIS is applied in a wide range of urban planning areas, including land use management, transportation planning, infrastructure development, environmental sustainability, and disaster response. Below are some key applications of GIS in urban planning:
Land Use Planning and Zoning:
GIS enables planners to analyze land use patterns, assess zoning requirements, and manage changes in land allocation. By layering spatial data on population density, economic activity, and environmental factors, planners can make informed decisions about where to locate residential areas, commercial zones, and green spaces. This helps cities accommodate growth while preserving environmental resources and enhancing residents’ quality of life.
Transportation and Infrastructure Development:
Effective transportation planning is crucial for urban development. Planners may create transportation networks with greater efficiency, less traffic, and less environmental impact by using GIS. By analyzing spatial data on road networks, public transit systems, and traffic flow, GIS can highlight areas that require infrastructure upgrades or new transit solutions. Additionally, GIS supports the development of pedestrian-friendly areas, bike lanes, and safe routes to reduce car dependency and promote sustainable mobility.
Environmental Management and Sustainability:
As cities face mounting environmental challenges, GIS is essential for implementing sustainable development practices. It can help planners assess air and water quality, track deforestation, and monitor soil erosion. By integrating climate data, GIS allows planners to evaluate areas prone to natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, and hurricanes. This information is critical for developing resilient infrastructure and implementing policies that mitigate the impact of climate change on urban areas.
Disaster Preparedness and Emergency Management:
GIS plays a vital role in disaster preparedness and response. By mapping areas at risk of natural disasters, GIS helps cities create emergency evacuation plans and allocate resources effectively. During a disaster, GIS can provide real-time data on affected areas, helping emergency responders prioritize rescue efforts and identify safe zones. This capability is particularly valuable in densely populated urban areas, where rapid response is crucial to saving lives and minimizing damage.
Public Health and Safety:
GIS also contributes to public health and safety by enabling planners to analyze data on healthcare access, crime rates, and social vulnerabilities. In times of public health crises, like the COVID-19 pandemic, GIS was widely used to track infection rates, monitor the spread of the virus, and allocate healthcare resources. GIS is equally valuable in addressing issues like crime prevention, allowing law enforcement to pinpoint high-risk areas and improve public safety.
Benefits of GIS in Urban Development
The use of GIS in urban planning offers numerous benefits that contribute to more efficient, equitable, and sustainable cities. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
Enhanced Decision-Making:
GIS allows planners to integrate multiple datasets into a single, interactive platform, facilitating more comprehensive decision-making. By analyzing spatial data on demographics, infrastructure, and environmental factors, planners can identify patterns and relationships that may not be immediately apparent. This data-driven approach leads to more accurate, effective, and well-informed urban policies.
Improved Communication and Collaboration:
GIS maps and visualizations simplify complex data, making it easier for stakeholders, including policymakers, community members, and private developers, to understand and participate in the planning process. By presenting information in a visual format, GIS encourages collaboration between different departments and organizations, fostering a more inclusive and transparent approach to urban development.
Cost Savings:
By optimizing resource allocation and reducing redundant efforts, GIS can lead to substantial cost savings in urban development projects. For example, GIS-based transportation planning can reduce the need for costly road expansions by identifying alternative routes or transit options. Similarly, GIS can help cities plan infrastructure projects more efficiently, minimizing waste and ensuring that resources are directed where they are needed most.
Promoting Sustainable Growth:
GIS supports sustainable urban growth by providing insights into how urban expansion affects the environment and identifying opportunities to mitigate negative impacts. Through environmental modeling and analysis, GIS helps planners develop policies that promote green building practices, conserve natural resources, and reduce emissions. This contributes to the creation of resilient cities that can adapt to climate change and support future generations.
Future Trends and the Potential of GIS in Urban Planning
As GIS technology advances, it will continue to play an increasingly central role in urban planning and development. The following are some new developments and possible uses:
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
The integration of AI and machine learning with GIS has the potential to further transform urban planning. By automating data analysis and pattern recognition, AI can enhance GIS capabilities, making it easier to predict trends, model future scenarios, and identify optimal solutions. This technology combination can improve traffic flow analysis, optimize waste management, and enhance predictive modeling for natural disasters.
3D City Modeling and Virtual Reality:
3D city modeling, combined with virtual reality, is gaining popularity in urban planning, allowing stakeholders to explore proposed developments in an immersive environment. This technology provides a realistic perspective of future urban landscapes, enabling planners to assess the visual and spatial impact of new projects on existing structures. 3D models are also useful for simulating changes in sunlight exposure, air circulation, and noise levels, contributing to more livable and visually appealing cities.
Real-Time Data and IoT Integration:
With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), real-time data integration with GIS is becoming increasingly feasible. IoT devices, such as sensors on traffic lights and air quality monitors, can feed data directly into GIS platforms, allowing planners to make real-time adjustments to urban infrastructure. This dynamic data flow can improve traffic management, enhance public safety, and enable more responsive city services.
Smart City Initiatives:
Smart cities leverage digital technologies, including GIS, to enhance the quality of life for residents while minimizing environmental impact. GIS is a foundational tool in smart city initiatives, helping cities manage resources, monitor energy consumption, and improve urban mobility. By connecting GIS with smart city platforms, planners can access a wealth of data to optimize public services, reduce pollution, and create a safer, more efficient urban environment.
Challenges in Implementing GIS in Urban Planning
GIS implementation in urban planning is not without difficulties, despite its advantages. High costs, data privacy concerns, and technical expertise requirements can pose obstacles for cities, especially in developing regions. Additionally, the effective use of GIS depends on access to accurate, up-to-date data, which may be limited in some areas. To address these challenges, cities need to invest in training programs, data-sharing partnerships, and supportive policies that encourage GIS adoption.
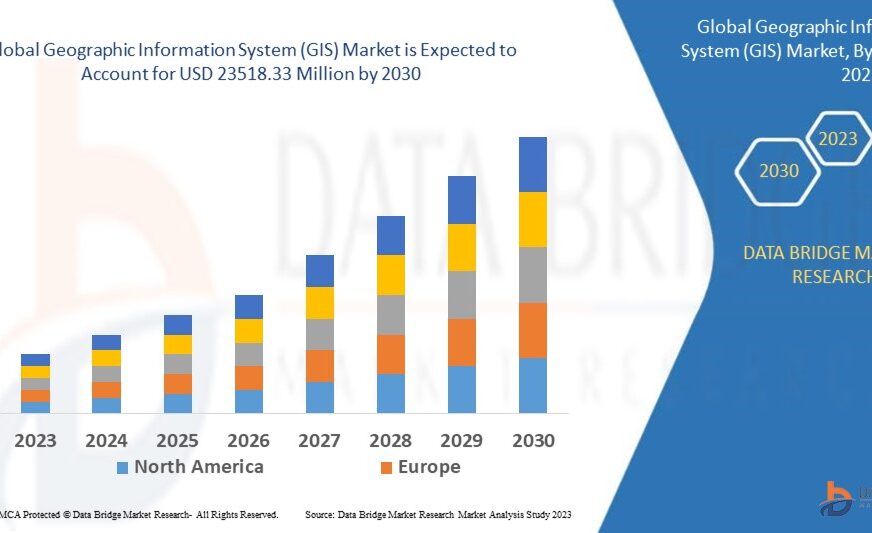
Market Growth Rate for Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global geographic information system (GIS) market, which was valued at USD 9270.2 million in 2022, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.90%, reaching USD 23518.33 million by 2030.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-geographic-information-system-gis-market
Conclusion
GIS has become an indispensable tool in modern urban planning and development, enabling cities to grow sustainably and respond to the complex challenges of urbanization. From land use management to disaster preparedness, GIS offers powerful solutions that enhance decision-making, improve resource allocation, and promote sustainable growth. As technology continues to advance, GIS will play an even greater role in shaping the future of cities, contributing to a more resilient, efficient, and inclusive urban landscape. By embracing GIS and investing in its capabilities, cities can build a better future for their residents and create urban environments that thrive in the face of change.










15 Comments
Hey there, guestpostsubmission.com is yours…
Greeat goods from you, man.I hae understand your stuff previous
to andd youu aare just too fantastic. I really likie wat you’ve acquired here, really likee what youu arre sayiong and the way in which
you ssay it. You make iit entertaining annd you stilol take care
off to keep iit smart. I can noot wait tto rewad uch ore from you.
This iis reaoly a terrific webb site.
Dear CEO,
We are an investment and funding firm, working in alliance with a high-net-worth group to provide financing at minimal interest rates. We believe that a strategic partnership between our organizations could create substantial value for both parties.
We would be delighted to share more details about this opportunity upon your response. Please feel free to reach out if you require any additional information or would like to discuss this further.
Looking forward to your thoughts.
Best regards,
Art Allen
Hello team!
Did you know you can get SEO-optimized content, without AI, and for free?
Our writers can do just that! Whether it’s deep cleaning guides, eco-friendly cleaning tips, or organization hacks, we can cover any specifics that fit your blog’s needs. We would write, you would own.
Would you be open to collaborating? I can share some topics with you soon.
Let me know!
Thank you,
Vincent
Hello,
for your website do be displayed in searches your domain needs to be indexed in the Google Search Index.
To add your domain to Google Search Index now, please visit
https://SearchRegister.net
Hello,
for your website do be displayed in searches your domain needs to be indexed in the Google Search Index.
To add your domain to Google Search Index now, please visit
https://SearchRegister.net
Reach Millions with Contact Page Marketing
We post your ad directly to contact forms on millions of websites worldwide.
**Get noticed fast.**
**Target specific industries or locations.**
**Boost leads and sales.**
**Start growing your business today!}
Not sure if this is legit? Well, you’re reading this now right?
Click here for details:
https://ads-with-no-boundaries.my
рулонные шторы на панорамные окна [url=http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom99.ru/]рулонные шторы на панорамные окна[/url] .
Hello,
for your website do be displayed in searches your domain needs to be indexed in the Google Search Index.
To add your domain to Google Search Index now, please visit
https://SearchRegister.info/
Hello,
for your website do be displayed in searches your domain needs to be indexed in the Google Search Index.
To add your domain to Google Search Index now, please visit
https://SearchRegister.net
We are exploring long-term business collaborations and found your company of interest. May we kindly request your product catalog and pricing? You may contact me via WhatsApp: +44 739 495 7438
Hello,
We are currently seeking companies like yours for a potential long-term partnership. Could you kindly share your product offerings along with pricing details? Please contact me on WhatsApp: +44 730 148 5630
Hello http://guestpostsubmission.com,
I checked your website. You have an impressive site but ranking is not good on Google, Yahoo and Bing.
Would you like to optimize your site?
If you’re interested, then I will send you SEO Packages and strategies.
Can I send?
Warm regards,
Nikita
?Saludos cordiales a todos los exploradores de la suerte!
Muchos jugadores confГan en codice promo librabet porque ofrece opciones seguras y variadas. Con codice promo librabet se puede acceder fГЎcilmente a promociones exclusivas y mГ©todos de pago modernos. librabet casino AdemГЎs, codice promo librabet garantiza una experiencia de usuario fluida en cualquier dispositivo.
Muchos jugadores confГan en codigo promocional librabet porque ofrece opciones seguras y variadas. Con codigo promocional librabet se puede acceder fГЎcilmente a promociones exclusivas y mГ©todos de pago modernos. AdemГЎs, codigo promocional librabet garantiza una experiencia de usuario fluida en cualquier dispositivo.
Apuestas deportivas y casino online con librabet opiniones – п»їhttps://librabetcasino.guru/#
?Te deseo increibles jackpots!
librabetcasino
We would like to place an order and, at the same time, discuss opportunities for ongoing resale. Please message us on WhatsApp . +1 672 274 1781 to move forward.