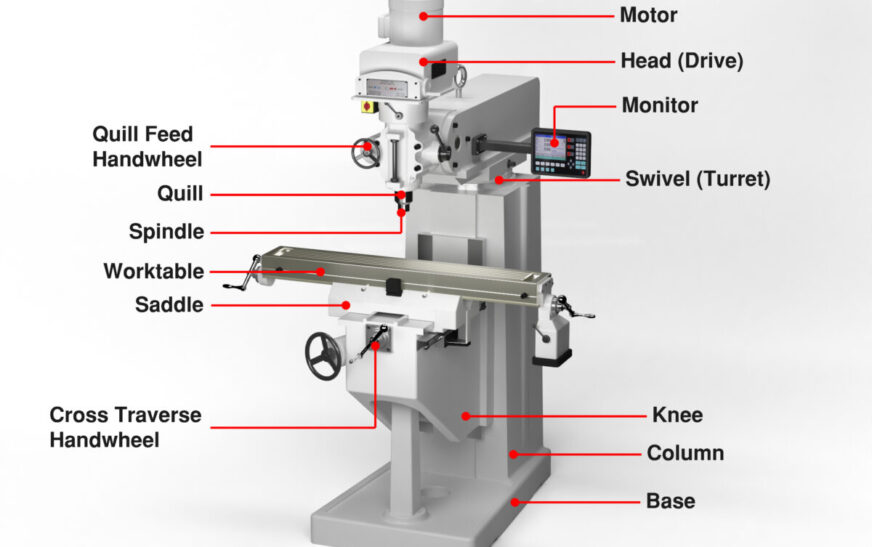
Milling machines are integral to modern manufacturing, providing the precision, versatility, and efficiency required to create a vast array of products across industries. From aerospace components to automotive parts and consumer electronics, milling machines play a critical role in shaping the world around us. This article will explore what milling machines are, the different types, their applications, and the benefits they bring to the manufacturing sector.
What Are Milling Machines?
Milling machines are versatile machines used in machining operations to cut and shape materials, typically metals, using rotary cutters. The process involves removing material from a workpiece by feeding it against a rotating cutting tool. Milling machines can perform a variety of functions, including drilling, cutting, shaping, and planing, depending on the complexity of the task and the type of machine.
These machines can be operated manually, CNC (Computer Numerical Control), or even in hybrid forms. The versatility of milling machines allows manufacturers to produce a broad range of products, from simple components to intricate parts with complex geometries. Milling machines are commonly used in industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer goods manufacturing.
Types of Milling Machines
There are several types of milling machines, each designed for specific applications. The primary difference between the machines lies in the arrangement of the cutting tool, the workpiece, and the machine’s overall design. Below are some of the most common types of milling machines:
1. Vertical Milling Machines
Vertical milling machines are characterized by a vertically oriented spindle. This type of machine is commonly used for tasks that require precision drilling and cutting along vertical axes. The most notable feature is that the cutting tool moves up and down, while the workpiece remains stationary.
Applications:
- Drilling and boring holes in a workpiece.
- Creating slots, grooves, and other features along vertical axes.
- Producing small, precise parts with detailed geometry.
Advantages:
- Excellent for precision work and smaller parts.
- More flexible for varied tasks such as drilling and milling.
- Easier setup and operation for smaller-scale jobs.
2. Horizontal Milling Machines
Horizontal milling machines, as the name suggests, have a horizontal spindle that holds the cutting tool. These machines are typically larger than vertical machines and are well-suited for tasks that require heavy material removal and higher cutting speeds. The workpiece is mounted on a horizontal table, and the cutting tool is positioned perpendicular to the workpiece.
Applications:
- Heavy-duty cutting operations such as facing and slotting.
- Manufacturing large, complex parts with high precision.
- Suitable for operations requiring significant material removal.
Advantages:
- More robust than vertical milling machines, handling heavier workloads.
- Ideal for producing large parts with deep cuts.
- Can handle multiple tools simultaneously, improving efficiency.
3. CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines are controlled by computers rather than manual operation. These machines utilize a computer program to control the movement of the cutting tool, allowing for highly precise and repeatable machining processes. CNC milling machines can perform a wide variety of tasks, from simple to highly complex, and they are often used for mass production of components.
Applications:
- High-precision manufacturing of complex parts.
- Mass production of components with uniform quality.
- Ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Advantages:
- High precision and accuracy.
- Can perform complex cuts and shapes that would be difficult with manual machines.
- Capable of running multiple operations on the same part.
4. Universal Milling Machines
Universal milling machines are versatile machines that combine features of both vertical and horizontal milling machines. These machines can be adjusted to accommodate a wide variety of machining tasks by changing the spindle orientation or using various attachments and tools.
Applications:
- Creating complex parts that require both vertical and horizontal machining.
- Suitable for smaller production runs or custom manufacturing.
- Used in tool rooms and smaller machining shops for their flexibility.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to handle a wide range of milling tasks.
- Ideal for job shops or smaller operations requiring multi-axis capability.
- Can be used for both light and heavy-duty milling.
5. Turret Milling Machines
Turret milling machines feature a fixed, vertical spindle that can be moved horizontally. The key advantage of turret milling machines is that the cutting tool can be easily adjusted in multiple directions, making them ideal for creating parts with complex geometries. Turret machines are common in workshops and are especially useful for tasks requiring frequent tool changes.
Applications:
- Producing precise parts with complex shapes.
- Ideal for small to medium-scale production.
- Commonly used in industries that require frequent customization and smaller batches.
Advantages:
- High versatility for a wide range of tasks.
- Flexibility in adjusting the cutting tool’s position for different operations.
- Useful for smaller-scale, custom manufacturing.
Key Applications of Milling Machines
Milling machines are used across various industries for a wide range of applications. Here are some common areas where milling machines are critical:
1. Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies heavily on milling machines to produce parts with high precision and tight tolerances. Aircraft components, such as turbine blades, landing gear components, and fuselage parts, all require the accuracy and efficiency that milling machines provide. CNC milling machines are particularly beneficial in aerospace due to their ability to create complex parts with intricate geometries.
2. Automotive
In the automotive industry, milling machines are used to manufacture parts that require high precision and durability. Components such as engine blocks, transmission housings, and chassis parts are commonly machined using milling processes. The ability to produce complex shapes and perform heavy material removal makes milling machines invaluable in automotive manufacturing.
3. Medical Device Manufacturing
Milling machines play a significant role in the production of medical devices. From precision surgical tools to prosthetics and implants, the medical industry requires the highest level of accuracy and attention to detail, which milling machines provide. CNC machines, in particular, are used for their ability to create parts that must meet stringent regulatory and quality standards.
4. Consumer Electronics
Milling machines are essential in the production of electronic components, including housing for smartphones, laptops, and televisions. The precision of milling allows manufacturers to produce intricate and detailed parts with tight tolerances, which are necessary for modern consumer electronics.
5. Tool and Die Making
Milling machines are commonly used in the production of tools, dies, and molds. These machines help create the molds that are used in other manufacturing processes like injection molding and casting. The ability to shape hard materials with high precision is a significant advantage in tool and die making.
Benefits of Milling Machines
Milling machines offer a range of benefits that make them a preferred choice in many manufacturing processes:
1. Precision and Accuracy
One of the primary benefits of milling machines is their ability to produce parts with high precision and accuracy. The use of CNC technology ensures that parts are made to exact specifications, with minimal variation. This level of precision is crucial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing, where even the smallest deviation can result in failure.
2. Versatility
Milling machines can perform a wide variety of tasks, making them highly versatile. From simple drilling operations to complex multi-axis machining, milling machines can handle almost any task. Their ability to use different cutting tools and configurations allows them to be used across many industries and applications.
3. Cost-Effective for Large-Scale Production
While the initial cost of setting up a milling machine can be significant, they are cost-effective for large-scale production runs. The ability to produce multiple parts quickly and with minimal waste makes milling machines an efficient choice for industries that require high-volume manufacturing.
4. Customization and Flexibility
Milling machines, particularly CNC machines, offer a high degree of flexibility. Operators can easily change the tooling or adjust the settings to accommodate new designs or variations in a product. This makes milling machines ideal for industries where custom parts or prototypes are required.
5. Durability and Reliability
Milling machines are built to handle rigorous and repetitive operations. Their robust construction ensures that they can operate for extended periods without compromising on performance. This durability makes milling machines a long-term investment for manufacturers.
Conclusion
Milling machines are indispensable in the world of manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, versatility, and efficiency. Whether it’s producing intricate medical devices, aerospace components, or automotive parts, milling machines help create high-quality products with tight tolerances and complex geometries. With advancements in CNC technology, milling machines continue to evolve, allowing manufacturers to push the boundaries of what is possible in modern manufacturing. As industries continue to demand more precision and efficiency, milling machines will remain at the forefront of innovation in the manufacturing sector.