I. Introduction to ISO 27001 Certification
A. What is ISO 27001 Certification?
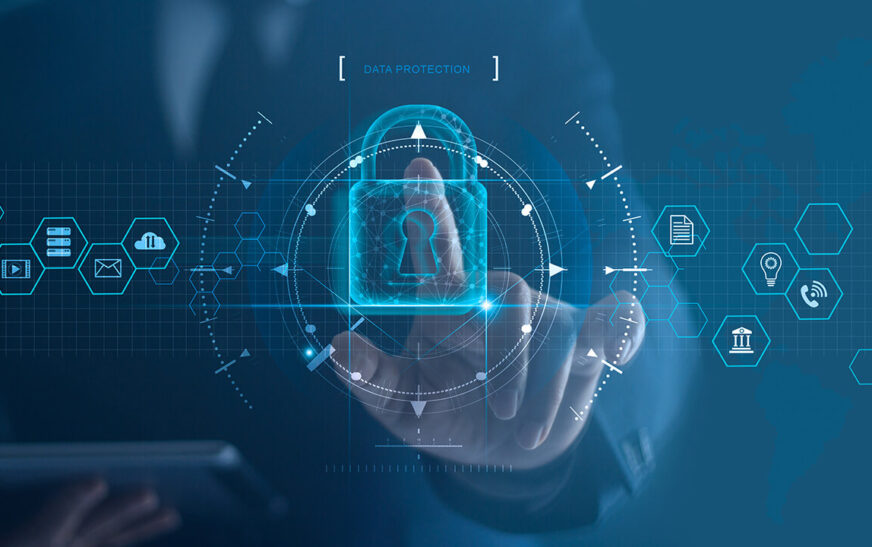
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It helps organizations manage and protect sensitive information, including personal, financial, and confidential data, from various security threats. Certification to ISO 27001 demonstrates an organization’s commitment to safeguarding information assets and maintaining robust security practices, which is increasingly critical in today’s digital landscape.
II. Benefits of ISO 27001 Certification
A. Improved data protection and risk management.
ISO 27001 certification enhances an organization’s ability to protect data by establishing a comprehensive approach to information security management. It involves identifying, assessing, and managing risks related to data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security threats. By implementing effective security controls and processes, organizations can better safeguard sensitive information and reduce the likelihood of data loss or compromise, thereby minimizing the impact of security incidents on the business.
B. Enhanced Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Certification to ISO 27001 helps organizations align their security practices with legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy.It ensures that businesses have the necessary measures in place to comply with local and international laws, such as GDPR and HIPAA.This alignment not only mitigates legal risks but also enhances organizational reputation and customer trust by demonstrating a commitment to protecting personal and sensitive data.
III. How ISO 27001 Enhances Information Security
A. Identifying and protecting sensitive information.
ISO 27001 helps organizations identify and categorize sensitive information, ensuring that it is appropriately protected. By understanding what data is most critical, businesses can implement tailored security measures to guard against unauthorized access, data leakage, and other vulnerabilities. This includes encrypting sensitive data, controlling access, and applying robust authentication protocols to ensure that only authorized personnel can access this information.
B. Implementing Measures to Prevent Data Breaches
To prevent data breaches, ISO 27001 establishes comprehensive security controls that minimize the risks associated with information security incidents. This involves adopting measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, secure email protocols, and employee training on best practices for data protection.By proactively managing these risks, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of a data breach and the potential impact on their operations.
III. How ISO 27001 Enhances Information Security
A. Identifying and protecting sensitive information.
ISO 27001 provides a structured approach to identifying and safeguarding sensitive information within an organization. By implementing a robust information security management system, organizations can effectively pinpoint what data is sensitive and prioritize measures to protect it. This includes classifying data, setting access controls, and ensuring proper data handling procedures. The standard emphasizes the importance of data protection through risk assessment and the development of security policies that mitigate potential threats. By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches and ensure that sensitive information remains secure.
B. Implementing measures to prevent data breaches.
To prevent data breaches, ISO 27001 outlines a comprehensive set of controls and procedures aimed at minimizing vulnerabilities and safeguarding organizational assets.These include technical controls such as firewalls, encryption, and antivirus software, as well as administrative controls like regular security training and awareness programs for employees.Additionally, ISO 27001 encourages the implementation of physical security measures, such as restricted access to data centers and secure storage facilities.By adopting a proactive approach to security, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of a data breach and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of their information systems.
IV. Key Steps to Implement ISO 27001
A. Management commitment and leadership involvement.
Successfully implementing ISO 27001 starts with strong management commitment and active leadership involvement. It is essential for organizational leaders to take ownership of the information security management system (ISMS) and demonstrate their support through dedicated resources, clear communication, and the allocation of appropriate funding.Leaders play a critical role in setting the strategic direction, providing the necessary guidance, and fostering a culture that prioritizes information security.They should be involved in key decision-making processes, support risk assessments, and ensure that security objectives are aligned with organizational goals.Without leadership commitment, even the best-designed security policies and procedures may struggle to gain traction or be effectively enforced.
B. Developing information security policies and procedures.
The development of comprehensive information security policies and procedures is a cornerstone of ISO 27001 implementation. These documents should outline the rules, guidelines, and protocols for managing information security across the organization. They should cover areas such as data protection, access control, incident management, and compliance requirements. Clear and concise policies provide a framework for employees and stakeholders to understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining information security. Procedures should be practical, well-documented, and regularly reviewed to adapt to new risks and changes in the business environment. This ensures consistency and compliance throughout the organization.
C. Implementing security controls and monitoring mechanisms.
Implementing security controls and monitoring mechanisms is crucial to safeguarding information assets under ISO 27001. These controls include technical, administrative, and physical measures designed to protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other security incidents. Examples include encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, regular security audits, and staff training. Monitoring mechanisms provide ongoing visibility into the security posture, enabling early detection of potential threats and swift responses. They also support continuous improvement by identifying areas where security controls may need enhancement. A proactive approach to implementing and monitoring these controls helps organizations maintain a robust security environment.
V. Continuous Improvement and ISO 27001
A. Creating a culture of continuous security improvement.
Achieving ISO 27001 certification is just the beginning of an organization’s information security journey. To maintain and enhance security, it is crucial to foster a culture of continuous improvement. This involves integrating security into the organizational mindset and encouraging all staff members to take ownership of information security practices. Continuous security improvement is about refining processes, addressing new threats, and adopting best practices as they evolve. It requires regular training, awareness programs, and open communication about security issues and incidents. By promoting a proactive attitude towards security, organizations can reduce vulnerabilities and ensure long-term resilience against emerging risks.
B. Monitoring security performance over time.
Monitoring security performance is a key component of maintaining ISO 27001 compliance and enhancing information security. It involves tracking various metrics, such as incident reports, access logs, and system performance, to gauge the effectiveness of security controls and procedures. Regular assessments help identify weaknesses, measure the impact of changes, and validate that security objectives are being met. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect their specific security goals and regularly review these to assess progress. This continuous oversight not only supports compliance but also drives the adaptation of security measures to address evolving threats and changing business needs.









1 Comment
The development of automated security orchestration and response tools has been a breakthrough for incident response teams. Watching how these systems can detect, analyze, and respond to threats in real-time is impressive. It’s helping security teams stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated attacks.