Introduction
In a world increasingly defined by remote work, hybrid teams, and global connectivity, the demand for smarter, more immersive collaboration tools has never been higher. Enter wearable conferencing technology—a game-changer that’s poised to redefine how we communicate, collaborate, and innovate in real-time. These futuristic yet rapidly advancing tools are not just about convenience; they are about enhancing productivity, reducing communication barriers, and enabling seamless interaction regardless of geography. From augmented reality glasses to smart earbuds with AI-powered translation, wearable conferencing technology is paving the way for a more connected and dynamic workplace.
Definition
Wearable Conferencing Technology refers to portable, body-worn devices – such as smart glasses, headsets, or wristbands – equipped with audio, video, and communication features that enable real-time virtual meetings and collaboration. These technologies allow users to participate in or host conferences hands-free, enhancing mobility and productivity, especially in remote work, field service, or healthcare environments.
The Evolution of Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools have evolved rapidly over the last two decades. From email and instant messaging to cloud-based platforms like Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams, each innovation has brought us closer together. However, despite their effectiveness, these tools still come with limitations—lag, screen fatigue, audio interruptions, and a lack of immersive interaction.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, but it also exposed the inadequacies of existing solutions. Workers struggled with the limitations of webcams, static presentations, and the lack of non-verbal communication. Wearable conferencing technology addresses these gaps by offering a more natural and intuitive way to interact.
What Is Wearable Conferencing Technology?
Wearable conferencing technology refers to hands-free, body-integrated devices that allow users to communicate and collaborate remotely. These can include:
- AR/VR headsets like Microsoft HoloLens or Meta Quest Pro
- Smart glasses that offer real-time video, facial recognition, and interactive overlays
- Wearable microphones and cameras for on-the-go audio-visual sharing
- Smart earbuds with noise cancellation and AI-driven language translation
- Body-worn sensors that track motion or convey non-verbal cues
These devices turn the user into an active part of the communication environment rather than a passive participant, making the interaction more realistic and engaging.
Benefits of Wearable Conferencing Technology
1. Enhanced Immersion and Presence
Traditional video calls provide a limited view—often a static head-and-shoulders shot with poor depth perception. Wearables, especially AR/VR devices, allow users to feel present in a virtual environment. A technician in Berlin can guide a worker in Tokyo through equipment repairs as if standing beside them. Teams can walk through 3D product prototypes together in real-time, no matter where they are.
2. Hands-Free Productivity
One of the most practical benefits is the hands-free functionality. Professionals in fields like healthcare, construction, and manufacturing can collaborate remotely without stopping their work to operate a device. A surgeon could get real-time input from global experts while in the operating room. Field technicians can receive instructions while keeping their hands on their tools.
3. Real-Time Language Translation and Voice Assistance
With embedded AI, many wearable devices can offer instant language translation and context-aware voice assistance, breaking down language barriers in global teams. Imagine a Japanese engineer speaking in their native language while a Brazilian colleague hears an English translation in real time through their smart earbuds.
4. Improved Data Sharing and Visualization
Wearables allow users to overlay digital information onto physical environments. This is especially useful in architecture, engineering, and design, where teams can view 3D models superimposed on real-world spaces or interact with virtual elements while discussing design revisions.
5. More Natural Non-Verbal Communication
Communication is more than just words—gestures, facial expressions, and posture carry critical meaning. AR and VR devices are increasingly capable of capturing and transmitting these cues, making remote meetings feel closer to in-person interactions.
Real-World Use Cases
Healthcare:
Doctors wearing smart glasses can live-stream surgeries to train medical students globally. Emergency responders can connect with specialists in real-time while treating patients on-site. Wearable conferencing tools are making telemedicine more effective, not just for consultations but also for complex procedures.
Manufacturing and Field Services:
Engineers and field workers can wear AR glasses to receive real-time guidance from off-site experts, reducing downtime and errors. Wearables also support remote inspections, diagnostics, and training, improving efficiency and safety in industrial settings.
Education and Training:
Educators can use VR headsets for immersive lessons, virtual labs, and collaborative group projects. Corporate trainers can simulate complex work environments for hands-on learning without physical constraints.
Remote Work and Team Collaboration:
Teams in different countries can meet in virtual environments, walk through interactive whiteboards, or co-develop projects using 3D modeling—all with a heightened sense of presence and engagement compared to 2D screen-based calls.
Challenges to Consider
Despite its promise, wearable conferencing technology does come with challenges:
- Cost: High-end devices like AR headsets are still expensive, though prices are gradually falling.
- Privacy and Security: Constant recording and data transmission raise concerns about surveillance and data breaches.
- Battery Life and Comfort: Many devices are still bulky or have limited battery life, making prolonged use difficult.
- Interoperability: With multiple platforms and standards, integrating wearables into existing systems can be tricky.
- User Adoption: Employees may resist change or feel uncomfortable using new technology without proper training.
However, as technology matures, many of these issues are being actively addressed by manufacturers and software developers.
The Future Outlook
The global market for wearable conferencing and collaboration technology is expected to grow exponentially in the coming years. According to industry forecasts, the wearable tech market is projected to exceed $150 billion by 2027, with a significant portion attributed to enterprise applications.
As 5G networks become widespread, edge computing advances, and devices get lighter and more powerful, we can expect wearables to become standard tools in modern workspaces. Companies like Apple, Google, Meta, and Microsoft are all investing heavily in this space—further signaling its future importance.
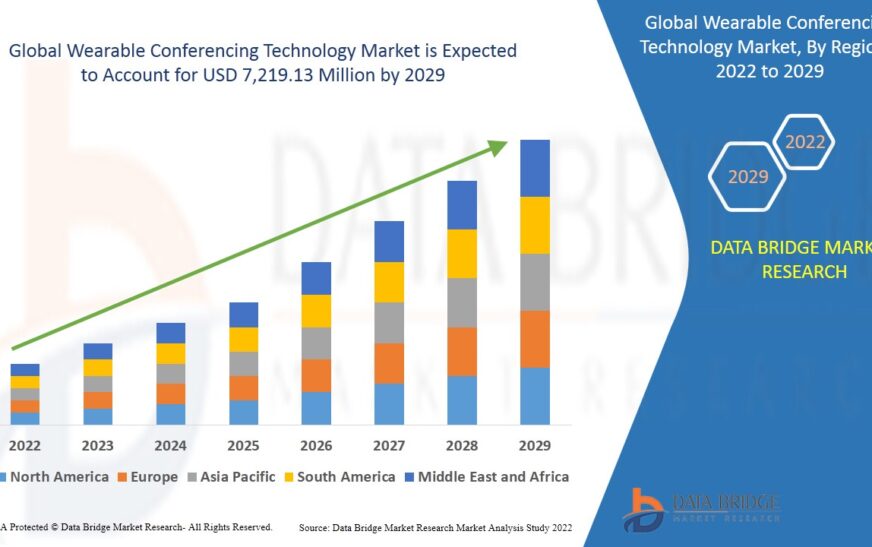
Growth Rate of Wearable Conferencing Technology Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the wearable conferencing technology market is anticipated to expand globally between 2022 and 2029. According to Data Bridge Market Research, the market is anticipated to reach USD 7,219.13 million by 2029, increasing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.9% from 2022 to 2029.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-wearable-conferencing-technology-market
Conclusion
Wearable conferencing technology represents the next leap in human collaboration. It merges the digital and physical worlds, providing a richer, more intuitive way for people to work together regardless of location. While adoption will take time and investment, the benefits—ranging from improved communication and productivity to reduced travel costs and greater accessibility—make it a transformative force in the future of work. As remote and hybrid work models become the norm, embracing wearable conferencing tools could mean the difference between staying competitive or falling behind in a fast-evolving digital landscape.