Introduction
In today’s digital world, email remains a primary mode of communication, used by individuals and organizations alike. However, the convenience of email also makes it a target for cybercriminals seeking to intercept sensitive information. This is where email encryption becomes an essential tool. By ensuring that emails are protected from unauthorized access, encryption safeguards privacy and enhances trust in communication. This comprehensive guide will explore what email encryption is, why it’s important, how it works, the different types of email encryption, and how to implement it effectively.
Definition
Email encryption is a method that incorporates security procedures into the DevOps process, in which teams from operations, security, and development work together to create, test, and implement safe infrastructure and apps. In the past, security was seen as a distinct stage of software development that usually came after coding. Email encryption, on the other hand, highlights the importance of integrating security into every stage of the development process, from design to deployment and upkeep.
What Is Email Encryption?
Email encryption is the process of encoding email messages to ensure that only authorized recipients can access and read them. This involves converting plaintext (readable text) into ciphertext (unreadable text) using cryptographic algorithms. The recipient, equipped with the appropriate decryption key, can then convert the ciphertext back into readable plaintext.
Encryption protects emails from unauthorized access, whether in transit or stored on servers. Without encryption, emails can be intercepted and read by malicious actors during transmission over networks.
Why Is Email Encryption Important?
Protecting Sensitive Information: Email encryption safeguards sensitive data such as financial details, personal information, and confidential business communications from being intercepted.
Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are governed by regulations that mandate the protection of sensitive data. For example, HIPAA requires encryption of emails containing protected health information, while GDPR emphasizes the importance of safeguarding personal data.
Preventing Data Breaches: Encrypting emails minimizes the risk of data breaches, which can lead to reputational damage, legal liabilities, and financial loss.
Ensuring Privacy: Encryption ensures that emails remain private, even if they are intercepted by hackers or monitored by unauthorized entities.
How Email Encryption Works
Email encryption relies on cryptographic techniques to secure communication. There are two main components involved:
Encryption Algorithms: Algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and RSA are used to encrypt and decrypt emails. These algorithms ensure robust security.
Encryption Keys: Keys are strings of data used in the encryption and decryption process. Email encryption typically involves:
- Public Key: Used to encrypt the email.
- Private Key: Used by the recipient to decrypt the email.
Types of Email Encryption
There are several types of email encryption methods, each with its own features and use cases:
1. Transport Layer Security (TLS):
TLS encrypts the connection between email servers, ensuring that emails are secure during transit. While widely used, TLS does not encrypt the actual content of emails, leaving them vulnerable if intercepted at endpoints.
2. End-to-End Encryption:
In end-to-end encryption, emails are encrypted on the sender’s device and can only be decrypted by the recipient’s device. This ensures complete security, as intermediaries cannot access the content. Popular protocols include:
- Pretty Good Privacy (PGP): Uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
- S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions): Relies on digital certificates for encryption and authentication.
3. Gateway Encryption:
Gateway encryption secures emails at the organization’s server before they are sent. The recipient’s email server then decrypts the messages. This approach is commonly used in enterprise environments.
Steps to Implement Email Encryption
- Choose an Encryption Method: Decide on the appropriate encryption method based on your needs. For individual users, end-to-end encryption is often ideal. For businesses, gateway encryption or TLS may be more practical.
- Enable Encryption in Your Email Client: Many email providers offer built-in encryption features. For example:
- Gmail: Supports TLS encryption by default.
- Outlook: Offers S/MIME encryption for enhanced security.
- Use Third-Party Tools: Tools like ProtonMail, Tutanota, and Mailfence provide end-to-end encryption and are user-friendly.
- Obtain Digital Certificates: For S/MIME, you need to obtain digital certificates from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to authenticate your email address and encrypt messages.
- Train Users: Ensure users understand how to use encryption tools and recognize potential threats like phishing attempts.
Best Practices for Email Encryption
To maximize the effectiveness of email encryption, follow these best practices:
Use Strong Passwords: Combine email encryption with strong, unique passwords to secure your accounts.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification.
Regularly Update Software: Keep email clients and encryption tools up to date to protect against vulnerabilities.
Encrypt Attachments: Use tools like PDF encryption or ZIP files with passwords to secure attachments.
Verify Recipients: Double-check recipient email addresses to avoid sending sensitive information to unintended parties.
Challenges of Email Encryption
Despite its benefits, email encryption faces some challenges:
- Complexity: Setting up encryption can be technically challenging for non-expert users.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all email providers support the same encryption standards, leading to potential interoperability problems.
- Key Management: Managing encryption keys requires diligence. Losing a private key can result in permanent loss of access to encrypted emails.
- Cost: Some encryption tools and digital certificates come with a cost, which may be a barrier for small businesses and individuals.
Future of Email Encryption
As cyber threats continue to evolve, email encryption is expected to become more widespread and user-friendly. Advances in quantum cryptography, machine learning, and artificial intelligence may pave the way for more robust and efficient encryption techniques. Additionally, growing regulatory pressure will likely push organizations to adopt encryption as a standard practice.
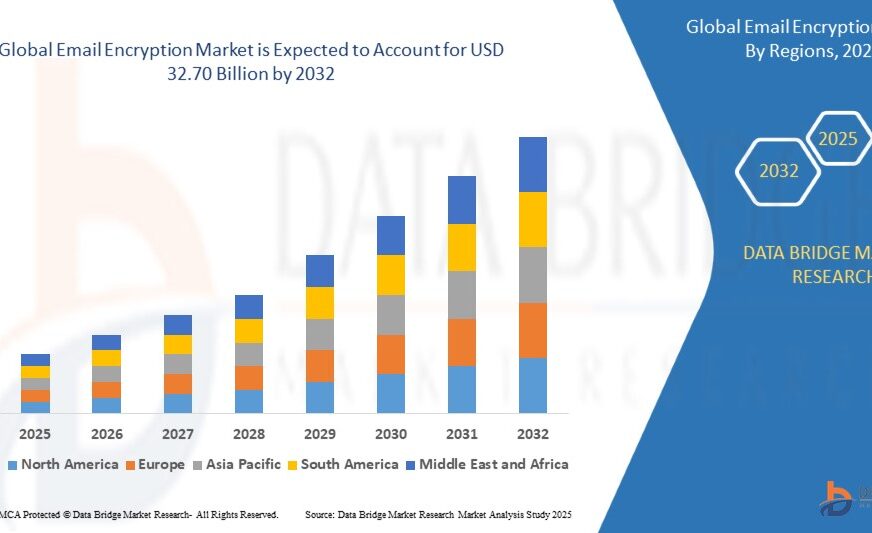
Growth Rate of Email Encryption Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global email encryption market was estimated at USD 7.55 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.10% from 2025 to 2032, reaching USD 32.70 billion.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-email-encryption-market
Conclusion
Email encryption is a cornerstone of secure communication in the digital age. By protecting sensitive information from prying eyes, it safeguards privacy, ensures compliance, and builds trust in email exchanges. While challenges exist, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, making encryption a necessity for individuals and organizations alike.